- Home
- About Us
- Products
&
Services
- Products
- Manual RO Water Treatment Plant
- Automatic RO Water Treatment Plant
- IoT enabled RO Water Treatment Plant
- Disinfection System for Municipal Water
- Deionization Water Treatment Plant (CDI)
- Custom-Engineered Water Treatment Systems
- Water Management Systems
- Water Conditioner and Softeners
- Sewage & Wastewater Treatment Plant
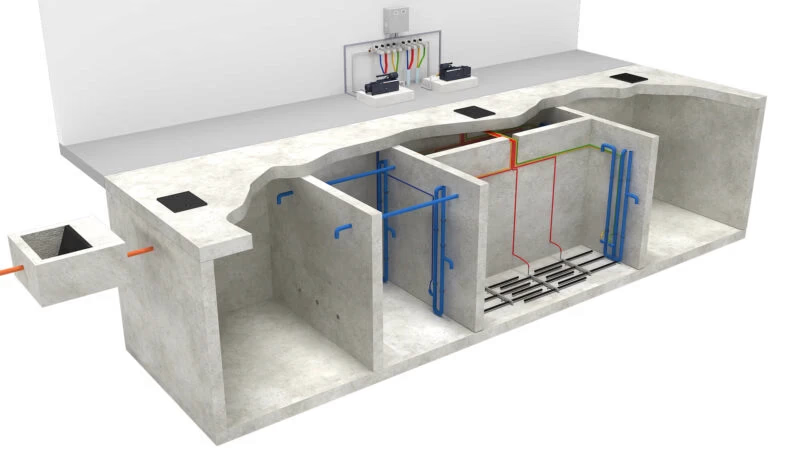
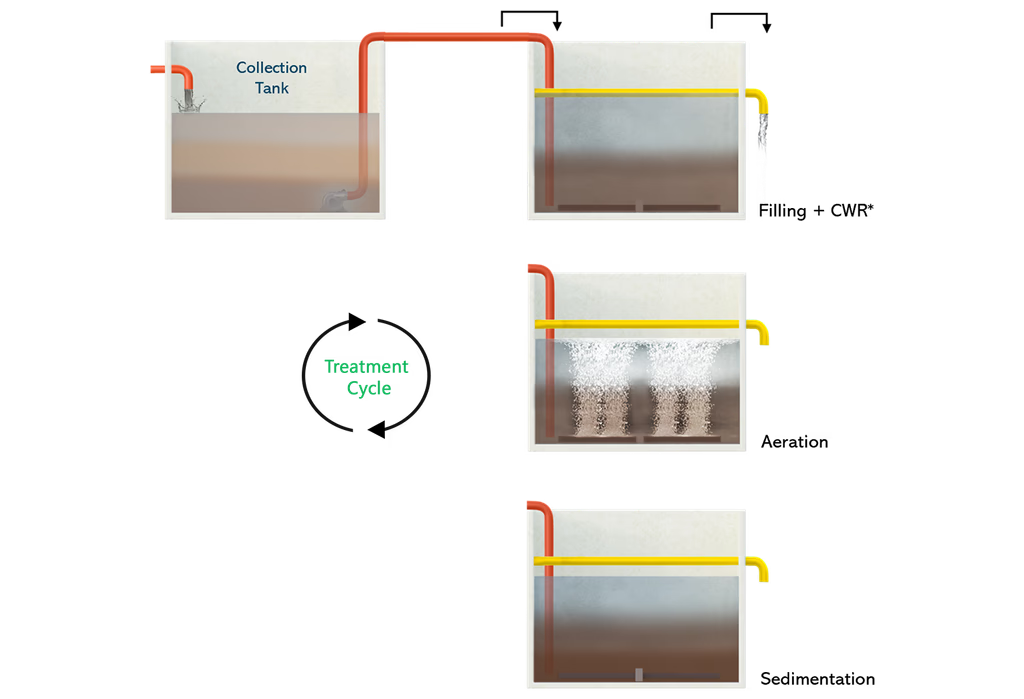
- Decentralised Waste Water Treatment System
- Services
- Products
- Turnkey Projects
- Contact Us
- Lake Restoration
- FAQ